什么是随机积分?(简版)
随机计算(stochastic calculus)是应用于随机过程(stochastic process)的运算,它对随机过程关于随机过程的积分作出定义,由日本数学家伊藤(Ito)创立。在本文中,我们将要对用布朗运动(Brownian motion)定义的随机积分进行一个简单的介绍,所用到的方式没有很强的技术性和理论性,目的是为了让尽可能多的人理解随机积分的概念。
1 布朗运动
布朗运动是指粒子在介质中的随机运动,它由植物学家布朗首次发现。这种运动模式通常包括粒子在流体(fluid)子域(sub-domain)内位置的随机波动,然后重新定位到另一子域。每次重新定位之后,新的子域中会出现更多波动。该模式描述了由给定的温度定义的处于热平衡(thermal equilibrium)的流体。在这种流体中,不存在优先流动方向。更具体地说,流体的整体线性动量(linear momentum)和角动量(angular momentum)随时间保持为零。
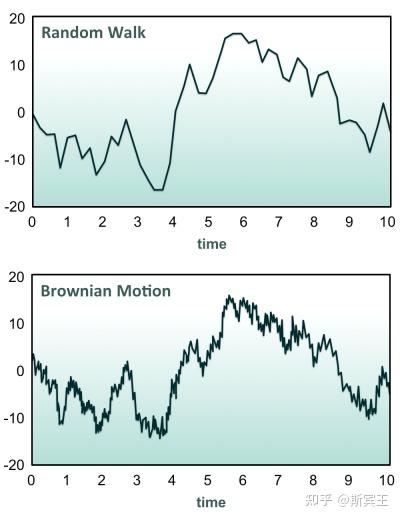
在数学中,布朗运动又叫维纳过程(Wiener process),它是一个连续时间(continuous-time)随机过程。布朗运动有很多种构造方式,在本文中,我们用随机行走(random walk)的极限来引入布朗运动。
定义 1.1 令 




![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图15 \mathbb{E}[\xi_t]=0\ \forall\ t](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)


令 













令 





定义 1.2 若一个连续时间随机过程 






则 











则 

布朗运动有很多很好的性质。它不仅是马尔可夫过程(Markov process),还是鞅(martingale)。此外,布朗运动还有处处连续(everywhere continuous)处处不可导(nowhere differentiable)的性质。
2 随机积分
我们想要对用布朗运动来定义的函数进行积分和微分,故引入随机积分的概念。令 

















如果 



![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图127 [0,T]](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)

都是一个成立的定义。
这就是对随机积分或伊藤积分的定义的简单介绍。注意伊藤积分的定义和黎曼-斯蒂尔杰斯积分(Riemann-Stieltjes integral)的定义
十分类似,这里 

![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图137 [x_{n-1},x_n]](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)



在随机积分中,我们通常使用像 



首先,由于我们将 ![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图127 [0,T]](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)








![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图167 \sum_{n=1}^{N}(W_{t_n}-W_{t_{n-1}})^2=\frac{1}{N}\sum_{n=1}^{N}\sqrt{N}(W_{t_n}-W_{t_{n-1}})^2\xrightarrow[a.s.]{}T=\int_0^T\ dt](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)



我们还可以用其他随机过程,如扩散过程(diffusion process),定义随机积分。
定义 2.1 如果随机过程 






显然,对于扩散运动的微分形式,我们仍有 


3 伊藤引理
在微积分(calculus)中,如果我们想要计算定积分(definite integral),我们不是用黎曼积分的定义,而是用微积分基本定理(fundamental theorem of calculus) 





若将此展开式写为微分形式,由于 

令 






这里 ![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图221 \tau_n\in[t_{n-1},t_n]](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图223 \xi_n\in[X_{n-1},X_n]](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
令 






若采用微分形式,可表达为
如果 

所以,如果 









4 随机优化
微积分可以被应用于优化问题,而类似地,随机计算也可以被应用于随机优化(stochastic optimization)。随机优化中的变量是随机变量,而如果这个随机变量是由布朗运动定义的扩散运动,我们之前引入的随机积分概念就要发挥作用了。考虑如下问题
其中 








我们可以通过推导贝尔曼方程(Bellman equation)来解决此类动态规划(dynamic programming)问题。令
为 


![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图269 J(t,x)\approx\sup_y(f(t,x,y)\Delta t+\mathbb{E}_t[J(t+\Delta t,x+\Delta x)])](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图271 \Leftrightarrow 0\approx\sup_y(f(t,x,y)\Delta t+\mathbb{E}_t[\Delta J])](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)



![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图277 0=\sup_y(f(t,x,y)+\mathbb{E}_t[dJ]/dt)](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
根据伊藤引理, ![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图279 dJ=(J_t+J_xa+\frac{1}{2}\mathrm{tr}[J_{xx}B\Sigma B^\top])dt+J_xBdW_t](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图281 \mathbb{E}[dW_t]=0](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图283 \mathbb{E}_t[dJ]=(J_t+J_xa+\frac{1}{2}\mathrm{tr}[J_{xx}B\Sigma B^\top])dt](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
此贝尔曼方程又叫HJB方程。HJB方程可以帮助我们解决随机优化问题。如果 
定理 4.1 令 





![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图291 \mathbb{E}_0\left[\int_0^\infty|f(s,X_s,Y_s)|\ ds\right]<\infty](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)

![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图293 \lim_{T\to\infty}\mathbb{E}_t\left[J(T,X_T)\right]=0](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
当 

证明根据HJB方程, ![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图301 f(s,X_s,Y_s)\le-(J_t+J_xa+\frac{1}{2}\mathrm{tr}[J_{xx}B\Sigma B^\top])](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)


![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图307 \int_t^Tf(s,X_s,Y_s)\ ds\le\int_t^T-(J_t+J_xa+\frac{1}{2}\mathrm{tr}[J_{xx}B\Sigma B^\top])\ ds](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图281 \mathbb{E}[dW_t]=0](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图311 =-\mathbb{E}_t\left[\int_t^T(J_t+J_xa+\frac{1}{2}\mathrm{tr}[J_{xx}B\Sigma B^\top])\ ds+J_xBdW_s\right]=J(t,X_t)-\mathbb{E}_t[J(T,X_T)]](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图279 dJ=(J_t+J_xa+\frac{1}{2}\mathrm{tr}[J_{xx}B\Sigma B^\top])dt+J_xBdW_t](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)

![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图315 \lim_{T\to\infty}\mathbb{E}_t[J(T,X_T)]=0](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
![概率里d(x)是什么_概率里dx是什么意思插图317 \mathbb{E}_t\left[\int_t^\infty f(s,X_s,Y_s)\ ds\right]\le J(t,X_t)](https://sigusoft.com/wp-content/themes/justnews/themer/assets/images/lazy.png)
参考文献
[1] Steven E. Shreve. Stochastic Calculus for Finance II-Continuous-Time Models. Springer Finance. Springer, New York, 2004.
[2] Fwu-Ranq Chang. Stochastic Optimization in Continuous Time. Cambridge University Press, 2004.
2024最新激活全家桶教程,稳定运行到2099年,请移步至置顶文章:https://sigusoft.com/99576.html
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请联系我们举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 文章由激活谷谷主-小谷整理,转载请注明出处:https://sigusoft.com/91332.html