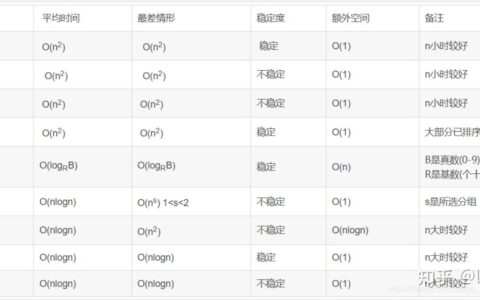
ECCET:Syllabus高级英汉/汉英翻译课程教学大纲 NANJING UNIVERSITY Professor KE, Ping Department of English, School of Foreign Studies, Nanjing University, 163 Xianlin Dadao, Nanjing, 210023, CHINA 22 Hankou Lu, Nanjing, 210093, CHINA EMAIL: kepingATnju.edu.cn Course Supporting Website: http://nlp.nju.edu.cn/kep/TOC/T.html; http://keping.sprinterweb.net/TOC/T.html English-Chinese & Chinese-English Translation (ECCET) CONTENTS E/C & C/E Translation (ECCET): Course Syllabus. 1 Course Objectives. 2 ECCET 1 – “Introduction to Translation” (Spring Semester) 3 ECCET 2 – “The Theory and Practice of Translation” (Fall Semester) 3 Course Resources. 3 Textbooks (required reading) 3 Suggested reading. 4 Short texts for translation. 4 Course website. 4 Methods of Instruction. 5 Assignments and Examination. 5 Requirements for Passing the Course and the Assessment Policy. 6 Course Schedule. 6 ECCET 1 – “Introduction to Translation” (Spring Semester) 6 ECCET 2 – “The Theory and Practice of Translation” (Fall Semester) 7 “英汉与汉英翻译”课程教学大纲… 9 教学目标… 9 ECCET 1 -“翻译导论”(春季学期) 10 ECCET 2 -“翻译理论与实践”(秋季学期) 10 课程资源… 10 教材 (必读书目) 10 推荐阅读书目… 11 翻译练习用短文… 11 课程网站… 11 教学方法… 11 作业与考试… 12 学习要求与考核方式… 12 教学单元与周历… 13 ECCET 1 -“翻译导论”(春季学期) 13 ECCET 2 -“翻译理论与实践”(秋季学期) 13 EC & C/E Translation (ECCET): Course Syllabus (Designed in line with the recommendations outlined in The National Syllabus for Instruction in English for College English Majors [2000] instituted by the English Subcommittee of China’s National Steering Committee for Teaching in Foreign Language Programs in Institutions of Higher Education) Time and Place: 14:00-15:50, Tuesday, spring and autumn semesters; Nanjing University Xianlin Campus. Instructor: Prof. Ke Ping [kepingATnju.edu.cn]. Office: Rm. 419, Qiaoyu Building, Nanjing University Xianlin Campus. Office hours: 12:00-13:50, Tuesday (by appointment). Rm. 210, Bld. Geng 庚字楼, Gulou Campus. English-Chinese & Chinese-English Translation (ECCET) is a core course offered to juniors and some Year 1 master students majoring in English Language and Literature or E/C Translation and Interpreting. The entire course is designed in a modular way and consists of two groups of modules (ECCET 1 – “Introduction to Translation” and ECCET 2 – “The Theory and Practice of Translation”). Each module group is taught in a separate spans two semester, with an examination administered and two credits awarded for the completed part of the course in each semester. Course Objectives The overall aim of the course is to cultivate students’ ability to perform real-life English/Chinese translation tasks. Theoretical and practical instruction is provided in translating written texts from English into Chinese and vice versa. At the end of the course, students are expected to be able to: ■ internalize [To take in and make an integral part of one’s attitudes or beliefs] the basic principles of translation, master the procedures and skills for analyzing source texts (especially difficult ones) and for generating appropriate target texts; ■ understand the similarities and differences between English and Chinese in morphology, syntax, textual structure, lexical and grammatical meanings, pragmatic conventions, rhetoric devices, and thought patterns, and acquire preliminary capabilities for handling culture-specific elements (realia) in the original; ■ develop an awareness of technical terms, knowing how to distinguish a term from a non-term and how to translate technical terms accurately; ■ command the skill of selecting and utilizing local and online reference tools as well as other aids and techniques developed for linguists and translators to solve complicated problems in translation; and ■ produce, independently and at the minimum speed of 250-350 words per hour for source texts of medium difficulty, translations that are on the whole accurate and complete in content, natural in expression, correct in terminology, and cohesive and coherent in textual structure. The course should also help to foster a strong sense of responsibility and a professional approach to tasks of practical translation work. Students are discouraged from working on by wild guessing or on superficial understanding of the original or wild guessing and will instead be instructed trained to fulfill translating and editing commitments in an honest and responsible committed way. Under the overall aim, instruction for in each of the two module groups semesters may have somewhat different focuses: ECCET 1 – “Introduction to Translation” (Spring Semester) Instruction at this stage is should primarily be concerned with helping students to understand the basic concepts and principles of translation and to develop the habit and capabilities to analyze source language expressions and sentences into their underlying syntactic structures, as well as to detect and decode the multiple meanings the source message may contain. By contrasting English with Chinese on the referential, pragmatic, and intralingual levels of meaning and signification, the instructor will alert the students to linguistic and cultural differences between the source language and target language, and help them to build up a basic capacity to translate textual elements tinged with local or historical color. Before the end of the semester, students are to should be given some systematic guidance on how to assess, select, and use local and online reference tools to solve linguistic and subject-matter knowledge complex problems in translation. ECCET 2 – “The Theory and Practice of Translation” (Fall Semester) A substantial part of the teaching of this module group instruction at this stage involves helping students to master the frequently used general rules to be followed as well as specific and strategies to be employed in addressing various problems the translator will encounter at the stage of frequently used in target text generation. as well as specific skills for rendering proper nouns, technical terms, and other special source elements into the target language. Students will learn how to use these rules and strategies, will and skills along with the procedures for source text analysis they learned in ECCET 1 the previous semester, to render properly into the target language complex source language/culture specific elements, proper nouns, technical terms, etc. in and other special source elements into the target language translate institutional, and technical texts (e.g. newspaper and journal articles related to government, economy, business, the press, diplomacy, science, law, etc.) as well as literary texts of moderate difficulty into the target language. Before the end of the semester, students will should receive some training in copy-reading (and, optionally, translating-editing). Another objective of the instruction at this stage is to further develop students’ competence to search for and utilize quality reference tools to resolve difficulties in translation. Depending on time available, a preliminary training in the use of CAT tools may also be introduced at this stage. Course Resources Textbooks (required reading) ECCET 1 – “Introduction to Translation” (Spring Semester) Zhuang, Yichuan (庄绎传). (1999).《英汉翻译教程》. 北京: 外语教学与研究出版社. vii+415 pp. Ke, Ping (柯平). (1991/1993).《英汉与汉英翻译教程》. 北京: 北京大学出版社. 206/209 pp. ECCET 2 – “The Theory and Practice of Translation” (Fall Semester) Newmark, Peter. (2001). A Textbook of Translation. 上海: 上海外语教育出版社 (First published 1988 by Prentice Hall International [UK] Ltd). xii+292 pp. [Sch. Lib.: J 19/W 58; 21871 外英PE-3] Sun, Wanbiao (孙万彪). (2003). 上海英语中级口译资格证书考试《中级翻译教程》. 上海外语教育出版社. xxvi+301 pp. Suggested reading ECCET 1 – “Introduction to Translation” (Spring Semester) Nida, E. A. & Taber, C. R. (2004). The Theory and Practice of Translation. 上海: 上海外语教育出版社 (First published 1969, 2003 by Koninklijke Brill NV, Leiden, The Netherlands). XII+220 pp. __. & Reyburn, William (1981). Meaning Across Cultures. American Society of Missiology Series, No. 4. NY: Orbis Books. 90 pp. [Univ. Lib.: B 961/W 14]. Tan, Zaixi (谭载喜). (1991). 《西方翻译简史》. 北京: 商务印书馆. 324 pp. __. (1999).《新编奈达论翻译》. 北京: 中国对外翻译出版公司. xxvi+342 pp. Yu, Yungen (喻云根). (1996).《英美名著翻译比较》. 汉口:湖北教育出版社. iii+432 pp. Zou, Zhenhuan (邹振环) (1996).《影响中国近代社会的一百种译作》. 北京: 中国对外翻译出版公司. 442 pp. ECCET 2 – “The Theory and Practice of Translation” (Fall Semester) Baker, Mona. (1992). In Other Words. A Coursebook on Translation. London & NY: Routledge. xix+654 pp. [ISBN: 0415030862; Amazon: $26.95] Nida, E. A. (1993). Language, Culture, and Translating. 上海: 上海外语教育出版社. [Univ. Lib.: H0/X22] Pinkham, Joan. (2000). Translator’s Guide to Chinglish (《中式英语之鉴》). 北京: 外语教学与研究出版社. vi+561 pp. Wang, Zuoliang (王佐良). (1989). 《翻译: 思考与试笔》. 北京: 外语教学与研究出版社. 213 pp. __. (1991). A Sense of Beginning: Studies in Literature and Translation (论新开端). 北京: 外语教学与研究出版社. 163 pp. Wilss, Wolfram. (1996). Knowledge and Skills in Translator Behavior. Amsterdam & Philadelphia: John Benjamins. viii+259 pp. {A clear discussion of various aspects of translation, including translator training, MT, etc.} [北图 2-97/ H 059 /W75; ISBN: 1556196962; Amazon: $87.00] Short texts for translation Available on course website. Course website http://keping.sprinterweb.net/TOC/T.html http://nlp.nju.edu.cn/kep/TOC/T.html Methods of Instruction Classroom teaching typically consists of lectures/discussions on one or more major theoretical/practical problems in English-Chinese and Chinese-English translation, and of instruction in both general principles and specific methods practitioners need to address those problems. The problems for lecture/discussions are selected and their sequence in classroom presentation determined on the basis of the difficulties real-life translators typically encounter at successive the different stages of a translation project, and of the judgments taken of the students’ language proficiency and cognitive receptability. To ensure that help the students apprehend those theoretical/practical problems in E/C translation are truly apprehended and as well as the principles and methods required to approach and address them mastereddeal with those problems, the instructor will may ask the students them to do some in-class translation exercises (with the text projected onto the projection screen) before carrying on with the lecturein-class exercises (usually projected onto the screen) in class will be assigned. By way of complementing classroom teaching, home assignments (including short-text translation exercises, or mini-research projects, and optional long translation project) will be assigned. Students will be asked are requested to present to the class their finished assignments take-/practicums / research projects they completed while the instructor will discuss in class the on students’ take-homework assigned and completed by the students without fail. Depending on time available, tutorial sessions may be arranged in each semester. The instructor will inspire should encourage students to explore into the principles and mechanisms underlying what they are learning at the operational level so that they can know not only the WHAT and HOW, but also WHY, of the general procedures followed and specific strategies employed in translation. Students are encouraged to pose questions or initiate discussions to the instructor as the class meets every week. Assignments and Examination Assignments for the course fall into three four types: (1) in-class translation exercises (designed to help students to consolidate what they have just learned from the lectures or class discussions); (2) take-home home assignments, including short-text annotation translation exercises (short texts of different genres, usually of 300-600 words, assigned to be translated out of class and discussed in class, to be assigned at an interval of two or three or four weeks) and/or mini-research projects; and (3) (optional) long translation project (real-life translator’s situation simulated in which students are required to translate out of class a full-length work or part of it within a period of time of 4 to 10 weeks).; and (4) end-of-semester research project or research paper (to be completed out of class in lieu of the final examination). Students are requested to complete all assignments on time. Late submission will result in a deduction from their scores for take-home coursework. Examination at the end of for the course in each semester will take the form of either the final examination (open-book) or the end-of-semester research project/paper. Requirements for Passing the Course and the Assessment Grading Policy Requirements for passing the course in each semester are as follows. (1) reading at least one textbook intensively and browsing through three items on the “Suggested Reading” list extensively each semester; (2) attendance at all class sessions and full participation in class activities (students are reminded that skipping classes might cause them to fail the course); (3) effective completion of all assignments, including in-class translation exercises and take-home assignments; and (4) passing the final examination / completing the end-of-semester research project or research paper. The assessment of a student’s performance in each semester Grading will be based on the following components: (1) attendance at and class, contribution to the class (responding to questions and raising good questions or suggestions, active involvement in class discussions, etc.), and completion of in-class translation exercises (15%); (2) scores obtained for presentations on in-class exercises and take-home assignmentsshort-text translation exercises, mini-research projects, and (if applicable) long translation projects (25%); and (3) scores obtained for the final examination, end-of-semester research project, or term paper (60%). Grades are calculated in real time with a computer spreadsheet program. Students can consult the instructor about the scores they have earned for the study of the course at any convenient time throughout each semester. Course Schedule * ECCET 1 – “Introduction to Translation” (Spring Semester; Course code: 10010150) Unit 1 Orientation (Week 1) Unit 2 Translation and the Translator (Weeks 2-3) ■ The concept of translation ■ Types of translation ■ The makings of a good translator ■ Mini-research: Sight translation of the transcript of Chinese Foreign Minister’s and Chinese Premier’s answers to media questions during the annual session of the National People’s Congress Unit 3 What Qualifies to Be a Good Translation? (Weeks 4-7) ■ Basic semantics for translation ■ Translation standard Mini-research: Library study of resources for studying translation Unit 4 Special Topics in Translation (Week 8) ■ Using reference tools in translating (1) ■ Mini-research: Comparative reading of source texts and their translations Unit 5 Source Text Analysis (1) (Week 9-14) ■ Intralingual factors involved in the analysis of the source text ■ Extralingual (non-cultural) factors involved in the analysis of the source text Unit 6 Tutorial (Week 15) Final Examination (Week 16) ECCET 2 – “The Theory and Practice of Translation” (Fall Semester) Unit 1 Orientation and Feedback (Week 1) ■ Course orientation ■ Instructor’s comments on the results of previous semester’s final examination in translation Unit 2 Source Text Analysis (2) (Weeks 2-3) ■ Source text analysis: Extralingual (cultural) factors involved in the analysis of the source text Unit 3 Target Text Generation (Weeks 4-10) ■ Word order ■ Deixis ■ Passive constructions ■ The choice of sentence subjects ■ Splitting and merging sentences ■ Compensatory procedures/devices ■ Mini-research: The use of reference tools in translation End-of-semester Research work: The use of compensatory procedures in translating / research project: Field study of the translation of local publicity material Unit 4 Copy Editing (Week 11) ■ Checking the accuracy of the translation against the original ■ Removing translationese Unit 5 Special Topics in Translation (Weeks 12-16) ■ Using reference tools in translating (2) ■ Proper nouns and technical terms ■ Numerical expressions ■ Public signs and advertisements ■ Metaphors ■ Sound symbolism [Optional] ■ Translating-editing [Optional] ■ Error analysis [Optional] ■ Mini-research: Textual study of the translation of publicity material Unit 6 Tutorial (Week 17) End-of-semester Research Project or Final Examination (Week 18) * Depending on time available, a few topics listed above here may be not covered in class in the current academic year. (Page revised: April, 2008; February, 2009; May 2009; February, 2010; September, 2011; August, 2012; September, 2014; March, 2015; June, 2015; February, 2017; April, 2017, February, 2018; January, 2020) Instruction in English-Chinese and Chinese-English Translation starts from the second semester of the sophomore year and covers the following two phases: Phase 1 (the first and second semesters of the sophomore year): Elementary English-Chinese / Chinese-English Translation; Phase 2 (the first and second semesters of the junior year): Advanced English-Chinese / Chinese-English Translation. Grading Policy The assessment of the student’s work in this course will be conducted on a 50% to 50% basis (with the hundred-mark system adopted). This means that 50% of the total scores will be process scores and the remaining 50% scores result scores. Process scores will be earned by the student through attendance at class, prompt response to questions, full participation in class discussion, and effective completion of in-class and take-home assignments. Result scores will be determined by the final. 南京大学外国语学院英语专业课程 “英汉与汉英翻译”课程教学大纲 根据高等学校外语专业教学指导委员会英语组《高等学校英语专业英语教学大纲》[2000] 制定 课程时间与地点:春季与秋季学期每周二 14:00-15:50;南京大学仙林校区. 教师:柯平教授 [kepingATnju.edu.cn]. 办公时间:周二 12:00-13:50 (侨裕楼419;需预约) 柯 平 “英汉与汉英翻译”(ECCET)是为高等院校英语专业与翻译专业高年级本科生及部分一年级硕士生开设的一门核心课程。课程为模块化设计,完整课程由模块组一(ECCET 1 -“翻译导论”)和模块组二(ECCET 2 -“翻译理论与实践”)构成,分别在每学年的春季学期和秋季学期里教授。每学期课程独立选修与考核,通过者可获得两个课时学分。 教学目标 “英汉与汉英翻译”课程的总目的是在于为学生提供英汉和汉英笔译理论与实践方面的进阶高级指导,培养与提高他们完成笔头翻译任务的实际能力。修学完此课程成绩合格的学员应能够: ■ 理解消化并自觉依循翻译基本原理,掌握英汉复杂词语、句子和语篇的分析理解方法技巧,掌握生成合格译文的基本技能; ■ 从词法形式、句子结构、篇章结构、词义和语法意义、语用规范、修辞手段、思维逻辑等方面把握英汉两种语言的异同,具有处理原文中带有民族文化特色的语言成分的初步能力; ■ 具备术语意识,有辨识和准确翻译术语的能力; ■ 掌握本地和在线参考工具的使用以及独立从事英汉互译工作所需的其他技术与技能; ■ 以每小时250-350个英文单词的速度将中等难度的原文文本译成目标语文本,做到原文理解接近准确完整,译文表达规范,术语使用正确,篇章结构基本上自然连贯。 考虑到我国翻译界和教育领域内存在着的学风浮夸和学术一些造假与浮夸问题,任课教师还将身传言教,应注意培养同学良好的学术操行和严谨的工作作风与责任感,帮助他们摒弃避免不求甚解、望文生义、靠猜测与臆断做翻译,甚至胡编乱造的做法,培养成学生负责任地独立完成翻译与编校工作的意识与习惯能力。 在始终围绕课程总目标组织教学的前提下,两模块组内容每学期的教学可各有所侧重: ECCET 1 -“翻译导论”(春季学期;课程编号:10010150) 着重点帮助学生理解基本翻译概念与原理,培养他们分析原文深层句法结构及原文信息可能具有的多重意义的习惯与能力。通过在指称、语用和言内三个意义层面上对英汉语进行对比,使学生充分认识到英汉两种语言的异同,能辨识它们各自所属文化之间的差异,并初步获得处理原文中具有民族文化特色的成分的能力。此学期里教师还将指导学生学习如何鉴别和、选择和使用本地与在线参考工具,并使用这些工具来以帮助于解决翻译中的疑难复杂问题。 ECCET 2 -“翻译理论与实践”(秋季学期) 重点帮助学生掌握处理常用的译文生成阶段常见的各种问题的一般规则与具体策略,。技巧以及专名、术语等特殊词语的处理策略,使他们能够结合ECCET 1中上学期所教授学的原文分析方法,借助工具书与其他参考源,将政治、经济、商贸、新闻、外交、科技、法律、文学等领域内原文文本中的语言和文化特异性成分、专名、术语等复杂内容)政治、经济、商贸、新闻、外交、科技、法律、文学等领域内中等难度的原文文本完整译成恰当的目标语。学期结束前,教师将应安排一定时间指导学生进行学习译文审校与工作及编译工作(后者为可选内容)。在此阶段的翻译教学中,教师将需关注的另一个目标是继续注意培养学生搜寻与综合使用各类优质参考工具以解决翻译难题的能力。 课程资源 教材 (必读书目) ECCET 1 -“翻译导论”(春季学期) Zhuang, Yichuan (庄绎传). (1999).《英汉翻译教程》. 北京: 外语教学与研究出版社. vii+415 pp. Ke, Ping (柯平). (1991/1993).《英汉与汉英翻译教程》. 北京: 北京大学出版社. 206/209 pp. ECCET 2 -“翻译理论与实践”(秋季学期) Newmark, Peter. (2001). A Textbook of Translation. 上海: 上海外语教育出版社 (First published 1988 by Prentice Hall International [UK] Ltd). xii+292 pp. [Sch. Lib.: J 19/W 58; 21871 外英PE-3] Sun, Wanbiao (孙万彪). (2003). 上海英语中级口译资格证书考试《中级翻译教程》. 上海外语教育出版社. xxvi+301 pp. 推荐阅读书目 ECCET 1 -“翻译导论”(春季学期) Nida, E. A. & Taber, C. R. (2004). The Theory and Practice of Translation. 上海: 上海外语教育出版社 (First published 1969, 2003 by Koninklijke Brill NV, Leiden, The Netherlands). XII+220 pp. __. & Reyburn, William (1981). Meaning Across Cultures. American Society of Missiology Series, No. 4. NY: Orbis Books. 90 pp. [Univ. Lib.: B 961/W 14]. Tan, Zaixi (谭载喜). (1991). 《西方翻译简史》. 北京: 商务印书馆. 324 pp. __. (1999).《新编奈达论翻译》. 北京: 中国对外翻译出版公司. xxvi+342 pp. Yu, Yungen (喻云根). (1996).《英美名著翻译比较》. 汉口:湖北教育出版社. iii+432 pp. Zou, Zhenhuan (邹振环) (1996).《影响中国近代社会的一百种译作》. 北京: 中国对外翻译出版公司. 442 pp. ECCET 2 -“翻译理论与实践”(秋季学期) Baker, Mona. (1992). In Other Words. A Coursebook on Translation. London & NY: Routledge. xix+654 pp. [ISBN: 0415030862; Amazon: $26.95] Nida, E. A. (1993). Language, Culture, and Translating. 上海: 上海外语教育出版社. [Univ. Lib.: H0/X22] Pinkham, Joan. (2000). Translator’s Guide to Chinglish (《中式英语之鉴》). 北京: 外语教学与研究出版社. vi+561 pp. Wang, Zuoliang (王佐良). (1989). 《翻译: 思考与试笔》. 北京: 外语教学与研究出版社. 213 pp. __. (1991). A Sense of Beginning: Studies in Literature and Translation (论新开端). 北京: 外语教学与研究出版社. 163 pp. Wilss, Wolfram. (1996). Knowledge and Skills in Translator Behavior. Amsterdam & Philadelphia: John Benjamins. viii+259 pp. {A clear discussion of various aspects of translation, including translator training, MT, etc.} [北图 2-97/ H 059 /W75; ISBN: 1556196962; Amazon: $87.00] 翻译练习用短文 请从课程网站下载。 课程网站 http://keping.sprinterweb.net/TOC/T.html http://nlp.nju.edu.cn/kep/TOC/T.html 教学方法 课堂教学一般包括针对英汉和汉英翻译中一个或多个重要理论与实践问题展开的分析讲授与讨论,以及就译者处理这些问题时所应遵循的一般原则和所需采取要的具体手段而方面给予的讲授与指导。教师根据现实世界环境里译者在翻译项目实施过程的各个阶段须将要面对的主要困难以及具体授课对象的语言水平与认知理解能力选择课堂教授内容讲授与讨论的问题,并确定它们在教学过程中所处的相对先后顺序:一是现实世环境里译者在翻译项目完成过程的各个阶段中将要面对的各种主要困难及;二是对学生语言水平与认知理解能力的判断。为确保帮助学生理解与掌握处理上述理论与实践问题并掌握处理这些问题的原则和方法,教师将适时布置相关课堂练习(投影到屏幕上),随机指定同学报告将自己完成的练习结果唸给全班听,并对同学完成的练习进行实时给予讲评。 作为对课堂教学的补充,教师将定期布置供课后完成的短文翻译作业、小型研究作业或长篇翻译作业,并轮流指定安排同学课堂汇报告并讨论自己的作业结果。并教师将对课后作业中出现的问题进行分析与讲评。 教师可视具体情况安排课程辅导与答疑。 教师将启发和激应鼓励同学思考生探究翻译所学操作层面之下内容背后的原理和机制,以便不但知道具体翻译规程与策略“何为”、“如何”,而且知其“为何”。同学在每周的课上和课间提问及与教师进行学习交流将受到鼓励。 作业与考试 课程包括以下三四种形式的作业(采用第四种作业形式时不再举行课程期末考试): (1) 与讲授和讨论内容配套、帮助学生理解与巩固课堂讲授或讨论所学内容的课堂翻译练习; (2) 课后作业(包括不同文本类型的、每篇长度约为300-600字、文本类型各异的短文评注式翻译练习;每3-4周布置一次课后完成,课堂上同学报告,教师讲评以及小型研究作业); (3) (可选)长篇翻译作业(模拟现实世界中译者的工作状况,在4-10周时间内里连续翻译一部原文作品或其中的长篇选段,以综合锻炼学生解决真实翻译项目实施过程中可能会遇到的各种问题的能力;课后完成,课堂讲评讨论交流); (4) 期末研究项目或研究论文(综合运用课内所学内容与其他相关知识进行的研究性作业;课后完成)。 所有作业均须按时完成;不能完成或不能按时完成者课程平时成绩将被扣分。教师布置批改课后作业后一定进行课堂讲评。 考试形式为期末开卷笔试、期末研究项目或研究论文。 学习要求与考核方式 每学期修读本此课程修读合格的基本具体要求为: (1) 课前预习教材;,阅读推荐材料(每学期在该学期指定教材中选择至少一本精读,泛读三本推荐阅读材料); (2) 课堂专心听讲,积极提问和参与互动讨论;有事请假(提示:旷课可能导致课程成绩不及格); (3) 用心完成所有作业,包括课堂翻译练习和课后作业; (4) 通过期末考试 / 完成期末研究项目或研究论文。 课程成绩由以下几部分构成: (1) 课堂学习情况得分(根据到课情况及课堂提问、答问、参与讨论等情况评定)(15%); (2) 课堂练习与课后作业(包括短文评注式翻译练习与小型研究作业)得分(根据练习与作业的课堂报告评定)(25%); (3) 期末考试、期末研究项目或研究论文得分 (60%)。 课程成绩用计算机电子数据表软件实时计算管理,同学可于学期中任一合适时间向任课教师查询。 教学单元与周历 * ECCET 1 -“翻译导论”(春季学期) 第1单元 课程介绍 (第1周) 第2单元 翻译与译者 (第2-3周) ■ 翻译的概念 ■ 翻译类型 ■ 翻译工作对译者素质与能力的要求 ■ 小型研究作业:中国人大本年度例会期间外长和总理中外记者招待会现场口译内容文字整理稿视译 第3单元 什么是好的翻译 (第4-7周) ■ 翻译语义学基础 ■ 翻译标准 研究作业:图书馆翻译学习参考资料调查 第4单元 翻译专题 (第8周) ■ 翻译参考工具的使用 (1) ■ 小型研究作业:原文与译文对照阅读 第5单元 原文分析 (1) (第9-14周) ■ 影响原文理解的语内因素 ■ 影响原文理解的语外因素 (非文化因素) 第6单元 答疑 (第15周) 期末考试 (第16周) ECCET 2 -“翻译理论与实践”(秋季学期) 第1单元 介绍与讲评 (第1周) ■ 课程介绍 ■ 前一学期翻译课期末考试结果讲评 第2单元 原文分析 (2) (第2-3周) ■ 影响原文理解的语外因素 (文化因素) 第3单元 译文生成 (第4-10周) ■ 语序 ■ 指示关系 ■ 被动结构 ■ 主语的选择 ■ 句子的分合 ■ 补偿手段 ■ 小型研究作业:参考工具在翻译中的应用 研究作业:翻译补偿手段的使用 / 或 期末研究项目:本地外宣材料翻译实地调研 第4单元 校改 (第11周) ■ 校验译文 ■ 去除翻译腔 第5单元 翻译专题 (第12-16周) ■ 翻译参考工具的使用 (2) ■ 专名与术语 ■ 数字 ■ 公示语与广告 ■ 比喻 ■ 拟声词 [选讲题] ■ 编译 [选讲题] ■ 错译分析 [选讲题] ■ 小型研究作业:外宣材料翻译文本研究 第6单元 答疑 (第17周) 期末研究项目或期末考试 (第18周) * 视本学期时间充足与否,以上所列专题中的个别专题可能不作为课内讲授内容。 (修订时间:2008年4月;2009年2月;2009年5月;2010年2月;2011年9月;2012年8月;2014年9月;2015年3月;2015年11月;2017年2月;2017年4月;2018年2月;2020年1月)
2024最新激活全家桶教程,稳定运行到2099年,请移步至置顶文章:https://sigusoft.com/99576.html
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请联系我们举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 文章由激活谷谷主-小谷整理,转载请注明出处:https://sigusoft.com/19259.html