感兴趣的小伙伴可以先看看我的这篇文章哦,打开看看,说不定能帮到你一些~~
金陵科技学院软件工程学院软件工程专业
更新于2021.10.12晚:
之前写的那个版本的这几题非常的不规范,于是乎花了点时间重写了一下这几题,差点误导了各位(捂脸)。
1.(1):编写程序建立一个顺序表,并逐个输出顺序表中所有数据素的值。编写主函数测试结果。
实现代码:
#include <stdio.h> #define MAXSIZE 100 typedef struct{
int data[MAXSIZE]; int last; }sequenlist; sequenlist CreateSequenlist(int n){
int i; sequenlist L; printf("请输入%d个数:\n",n); for (i = 0;i < n;i++){
scanf("%d",&L.data[i]); } L.last = n-1; return L; } void PrintSequenlist(sequenlist L){
int i; for (i = 0;i <= L.last;i++){
printf("%d ",L.data[i]); } } int main(){
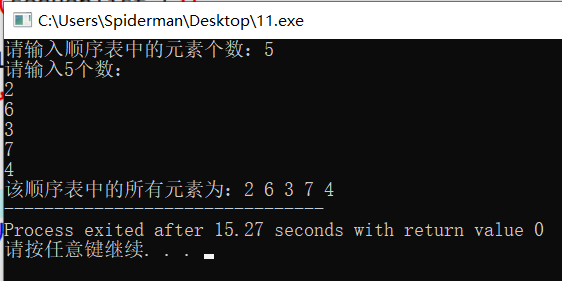
int n; printf("请输入顺序表中的素个数:"); scanf("%d",&n); sequenlist L = CreateSequenlist(n); printf("该顺序表中的所有素为:"); PrintSequenlist(L); return 0; } 运行结果:
分析:
该程序中用于输出顺序表中所有素的函数的时间复杂度与空间复杂度均为线性阶O(n)。
(2):编写顺序表定位操作子函数,在顺序表中查找是否存在数据素x。如果存在,返回顺序表中和x值相等的第1个数据素的序号(序号从0开始编号);如果不存在,返回-1。编写主函数测试结果。
实现代码:
#include <stdio.h> #define MAXSIZE 100 typedef struct{
int data[MAXSIZE]; int last; }sequenlist; sequenlist CreateSequenlist(int n){
int i; sequenlist L; printf("请输入%d个数:\n",n); for (i = 0;i < n;i++){
scanf("%d",&L.data[i]); } L.last = n-1; return L; } void PrintSequenlist(sequenlist L){
int i; for (i = 0;i <= L.last;i++){
printf("%d ",L.data[i]); } } int Search(sequenlist L,int x){
int i; for (i = 0;i <= L.last;i++){
if (x == L.data[i]){
return i; } } return -1; } int main(){
int n,x; printf("请输入顺序表中的素个数:"); scanf("%d",&n); sequenlist L = CreateSequenlist(n); printf("该顺序表中的所有素为:"); PrintSequenlist(L); printf("\n请输入想要查找的数据素:"); scanf("%d",&x); if(Search(L,x) != -1){
printf("顺序表中和该素值相等的第1个数据素的序号为:%d",Search(L,x)); }else{
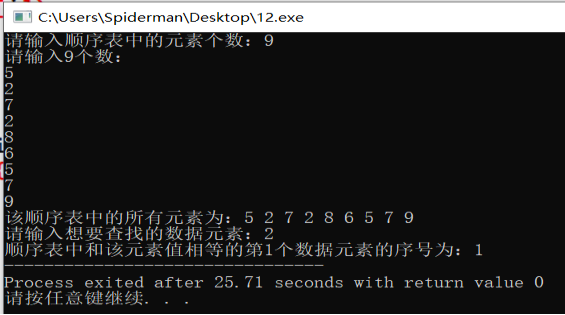
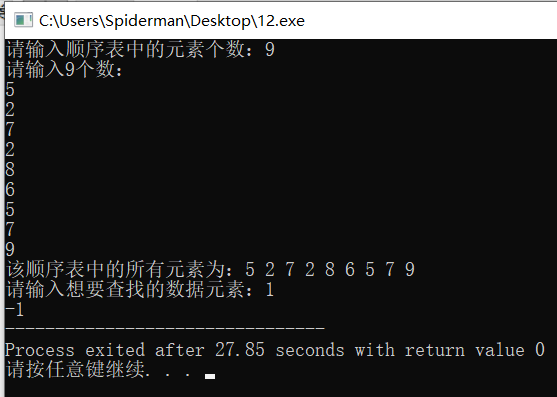
printf("%d",Search(L,x)); } return 0; } 运行结果:
分析:
该程序中顺序表定位操作子函数的时间复杂度和空间复杂度均为线性阶O(n)。
(3):在递增有序的顺序表中插入一个新结点x,保持顺序表的有序性。
解题思路:首先查找插入的位置,再移位,最后进行插入操作;从第一个素开始找到第一个大于该新结点值x的素位置i即为插入位置;然后将从表尾开始依次将素后移一个位置直至素i;最后将新结点x插入到i位置。
实现代码:
#include <stdio.h> #define MAXSIZE 100 typedef struct{
int data[MAXSIZE]; int last; }sequenlist; sequenlist CreateSequenlist(int n){
int i; sequenlist L; printf("请输入%d个数:\n",n); for (i = 0;i < n;i++){
scanf("%d",&L.data[i]); } L.last = n-1; return L; } void PrintSequenlist(sequenlist L){
int i; for (i = 0;i <= L.last;i++){
printf("%d ",L.data[i]); } } void Insert(sequenlist *L,int x){
int i,j,loc; for (i = 0;i <= (*L).last;i++){
if ((*L).data[i] > x){
loc = i; break; } } if (i > (*L).last){
loc = i; (*L).data[loc] = x; }else{
for (j = (*L).last;j >= loc;j--){
(*L).data[j+1] = (*L).data[j]; } (*L).data[loc] = x; } (*L).last++; } int main(){
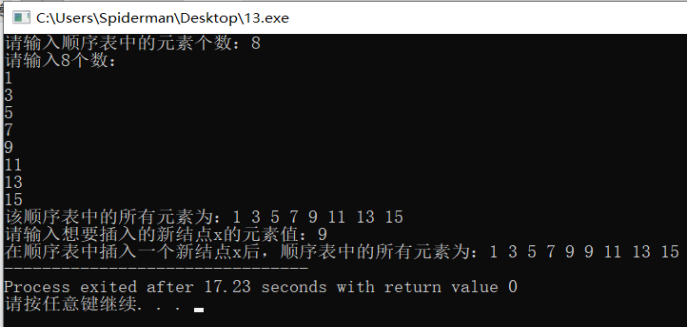
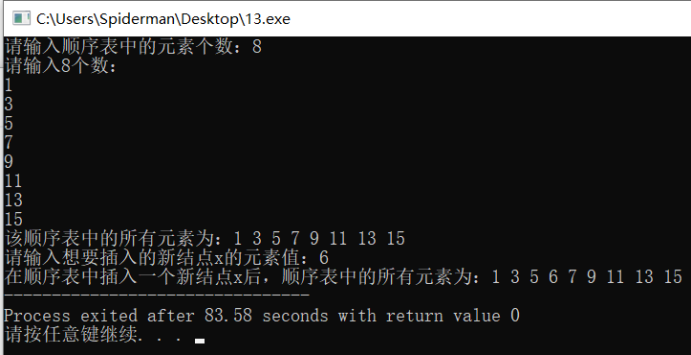
int n,x; printf("请输入顺序表中的素个数:"); scanf("%d",&n); sequenlist L = CreateSequenlist(n); printf("该顺序表中的所有素为:"); PrintSequenlist(L); printf("\n请输入想要插入的新结点x的素值:"); scanf("%d",&x); sequenlist *s = &L; Insert(s,x); printf("在顺序表中插入一个新结点x后,顺序表中的所有素为:"); PrintSequenlist(L); return 0; } 运行结果:
分析:
该插入操作的时间复杂度和空间复杂度均为线性阶O(n)。
(4):删除顺序表中所有等于X的数据素。
实现代码:
#include <stdio.h> #define MAXSIZE 100 typedef struct{
int data[MAXSIZE]; int last; }sequenlist; sequenlist CreateSequenlist(int n){
int i; sequenlist L; printf("请输入%d个数:\n",n); for (i = 0;i < n;i++){
scanf("%d",&L.data[i]); } L.last = n-1; return L; } void PrintSequenlist(sequenlist L){
int i; for (i = 0;i <= L.last;i++){
printf("%d ",L.data[i]); } } void Delete(sequenlist *L,int x){
int i,j,loc = -1; for (i = 0;i <= (*L).last;i++){
if (x == (*L).data[i]){
loc = i; for (j = loc+1;j <= (*L).last;j++){
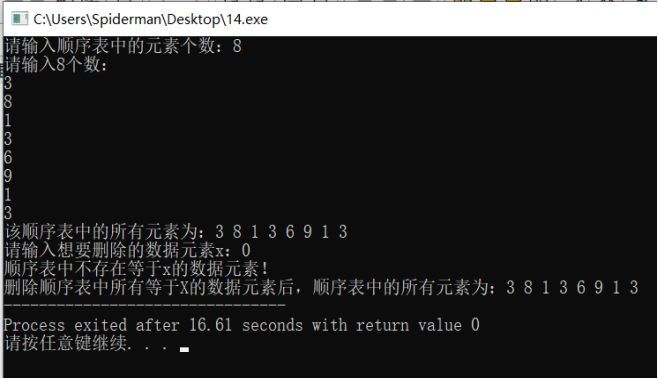
(*L).data[j-1] = (*L).data[j]; } (*L).last--; i--; } } if (loc == -1){
printf("顺序表中不存在等于x的数据素!\n"); } } int main(){
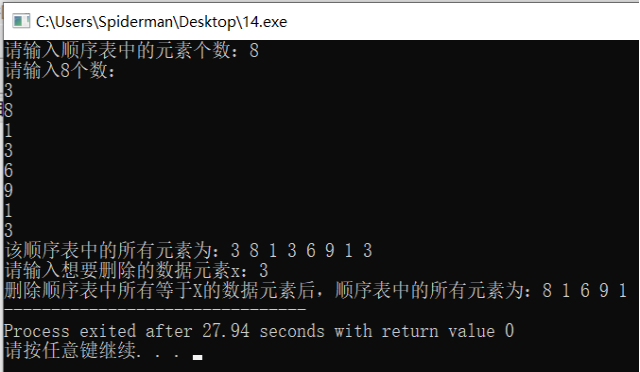
int n,x; printf("请输入顺序表中的素个数:"); scanf("%d",&n); sequenlist L = CreateSequenlist(n); printf("该顺序表中的所有素为:"); PrintSequenlist(L); printf("\n请输入想要删除的数据素x:"); scanf("%d",&x); sequenlist *s = &L; Delete(s,x); printf("删除顺序表中所有等于X的数据素后,顺序表中的所有素为:"); PrintSequenlist(L); return 0; } 运行结果:
分析:
该删除操作的时间复杂度为O(n²),空间复杂度为O(n)。
2.已知两个顺序表A和B按素值递增有序排列,要求写一算法实现将A和B归并成一个按素值递减有序排列的顺序表(允许表中含有值相同的素)。
实现代码:
#include <stdio.h> #define MAXSIZE 100 typedef struct{
int data[MAXSIZE]; int last; }sequenlist; sequenlist CreateSequenlist(int n){
int i; sequenlist L; if (n != 0 ){
printf("请输入%d个数:\n",n); for (i = 0;i < n;i++){
scanf("%d",&L.data[i]); } L.last = n-1; } return L; } void PrintSequenlist(sequenlist L){
int i; for (i = 0;i <= L.last;i++){
printf("%d ",L.data[i]); } } void MergeSequenlist(sequenlist *la,sequenlist *lb,sequenlist *lc){
int i = (*la).last,j = (*lb).last,k = 0; while(i!=-1&&j!=-1){
if((*la).data[i] >= (*lb).data[j]){
(*lc).data[k++]=(*la).data[i]; i--; }else{
(*lc).data[k++]=(*lb).data[j]; j--; } } while(i!=-1){
(*lc).data[k++] = (*la).data[i]; i--; } while(j!=-1){
(*lc).data[k++] = (*lb).data[j]; j--; } } int main(){
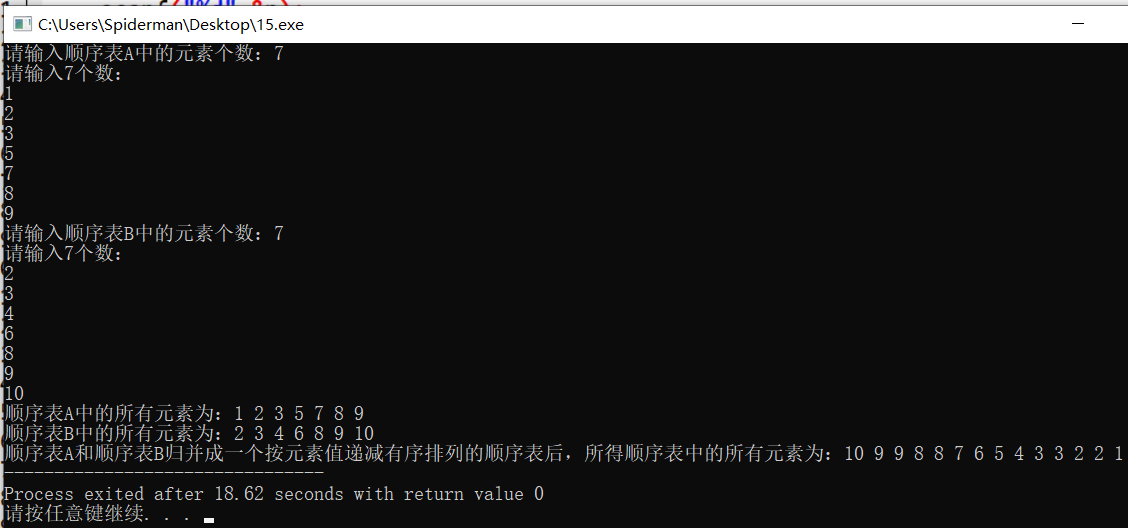
int n,m; printf("请输入顺序表A中的素个数:"); scanf("%d",&n); sequenlist A = CreateSequenlist(n); printf("请输入顺序表B中的素个数:"); scanf("%d",&m); sequenlist B = CreateSequenlist(m); printf("顺序表A中的所有素为:"); PrintSequenlist(A); printf("\n顺序表B中的所有素为:"); PrintSequenlist(B); sequenlist C = CreateSequenlist(0); C.last = A.last + B.last + 1; sequenlist *la = &A; sequenlist *lb = &B; sequenlist *lc = &C; MergeSequenlist(la,lb,lc); printf("\n顺序表A和顺序表B归并成一个按素值递减有序排列的顺序表后,所得顺序表中的所有素为:"); PrintSequenlist(C); return 0; } 运行结果:
分析:
假设顺序表A和顺序表B中均有n个素,则该归并操作的时间复杂度与空间复杂度均为线性阶O(n)。
2024最新激活全家桶教程,稳定运行到2099年,请移步至置顶文章:https://sigusoft.com/99576.html
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请联系我们举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。 文章由激活谷谷主-小谷整理,转载请注明出处:https://sigusoft.com/150997.html